
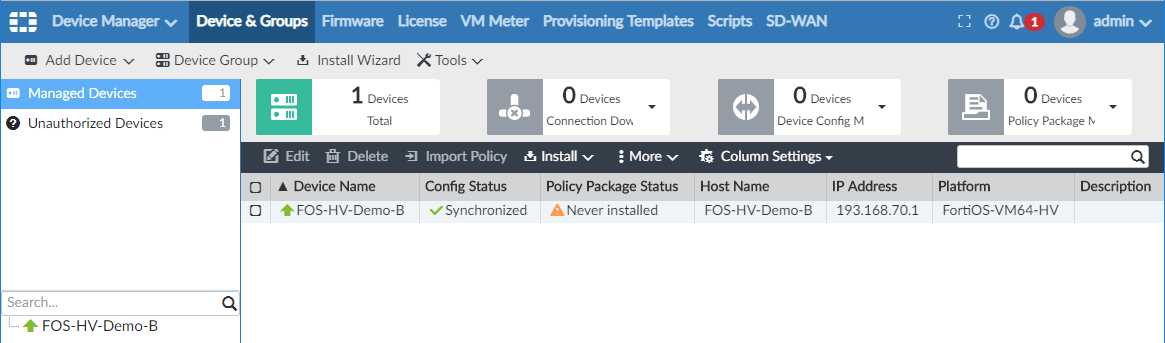
The following sections walk you through how to set up the FortiGate VM.
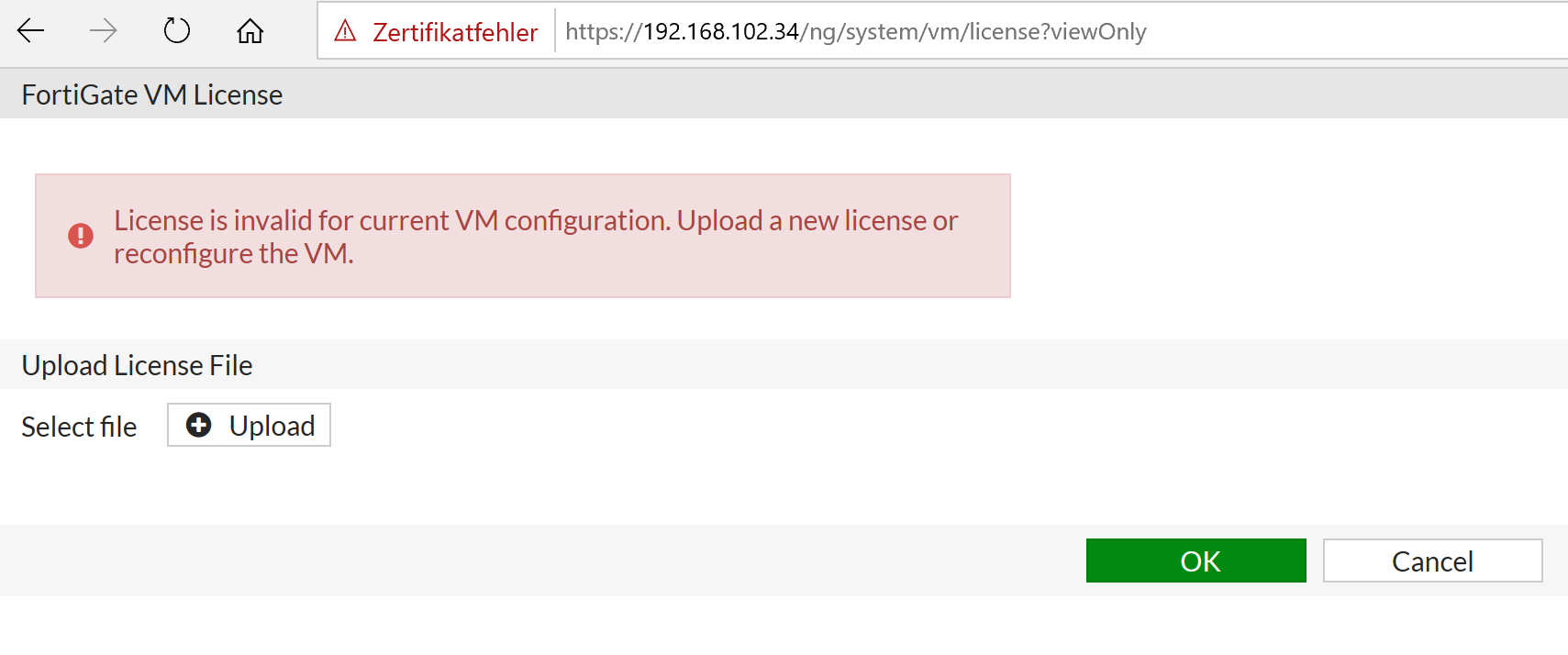
Select Create and attach network interface.Ĭonfigure properties for the new network interface and then select Create. In the menu on the left, select Networking. If the FortiGate VM is not already stopped, select Stop and wait for the VM to shut down. The Virtual Network in Azure on which the Virtual NIC resides must have a routable connection to those internal resources. The network interface is listed, and the inbound port rules are shown.Ĭreate a new inbound port rule for TCP 8443.įor internal resources to be made available to users, a second Virtual NIC must be added to the FortiGate VM. Create a New Inbound Network Security Group Rule for TCP Port 8443 This record maps to the preceding public IP address that is statically assigned. If you own a publicly routable domain name for the environment into which the FortiGate VM is being deployed, create a Host (A) record for the VM. On the Overview screen, select the public IP address. Go to the Azure portal, and open the settings for the FortiGate VM. In addition, map it to a fully qualified domain name (FQDN). Set a Static Public IP address and Assign a Fully Qualified Domain Nameįor a consistent user experience, set the public IP address assigned to the FortiGate VM to be statically assigned. Set Authentication type to Password, and provide administrative credentials for the VM. Select the software plan (bring-your-own-license if you have a license, or pay-as-you-go if not).
Select Fortinet FortiGate Next-Generation Firewall. Go to the Azure portal, and sign in to the subscription into which you will deploy the FortiGate virtual machine.Ĭreate a new resource group, or open the resource group into which you will deploy the FortiGate virtual machine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
